by Kevin Gaffney | May 14, 2024 | Blog Post
DDK is committed to providing the most robust and reliable GNSS augmentation service possible, we feel the only way to do this is use the optimum solution for each element of the service – with no compromise.
We are proud to announce that the final piece of the ‘jigsaw’ is now implemented as part of our service.
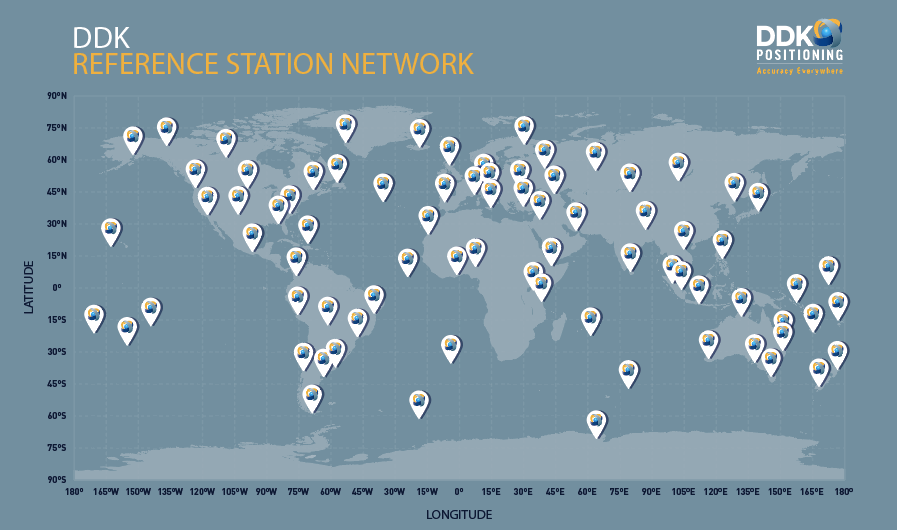
In addition to optimal global server solutions, Iridium delivery, Topcon GNSS hardware and in-house end to end navigation solutions we now have the addition of our GNSS network of reference stations and correction generation, ensuring optimal corrections are generated at the start point. The reference network stations are instrumental in providing a robust and reliable positioning service.
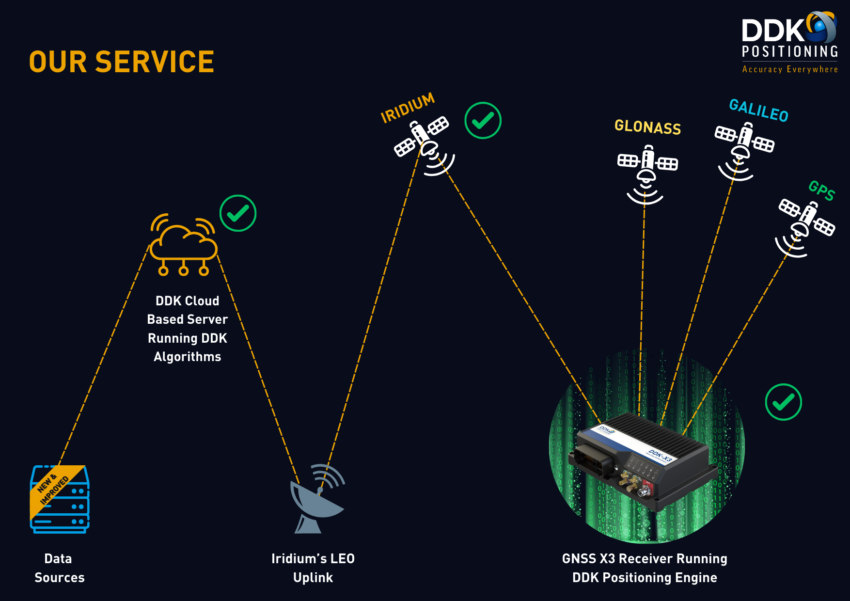
The 100+ globally distributed stations use sites selected to provide the optimum coverage for satellite tracking, multiple communication links, multiple state of the art GNSS receivers and backup power. This culminates in a level of redundancy that DDK is synonymous for and delivers professional level services to our end users.
Additionally the implementation of this network goes beyond the redundancy aspects of the service we provide. The use of this network of industry leading GNSS receivers as reference stations also delivers enhanced levels of accuracy for our services.
The tabulated results below are for a 24-hour period, as 5 different global locations.
Summary of results:
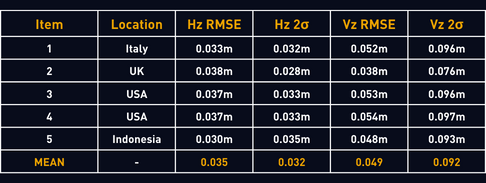
This enhanced level of service accuracy is a direct result of the latest GNSS infrastructure DDK operates and enables further enhancements to be implemented in the future.
Working with our partners Topcon and Iridium allows us to provide a positioning solution that is poles apart from the rest. By utilising our own reference station network, it allows us to provide the end user with increased accuracy and more importantly a positioning that is fully independent, robust and resilient.
For further information, please download the latest datasheet of our MAX service here or get in touch: info@ddkpositioning.com.

by Stuart Inglis | May 30, 2022 | Blog Post
Many things in life are given a second chance. Every time you pop something in the recycling rather than landfill it gets a second chance. You’ll have likely fallen out with a friend, family member or colleague at some point but have reconciled your differences and given them a second chance. Flares, SodaStream, Polaroids, Tamagotchis, lava lamps and even bumbags have seen a resurgence in desirability and been given a second chance…arguably some should have stayed in the 90’s, but you can be the judge on that!
However, in space, second chances are few and far between.
Once equipment is launched into space manual intervention is not an option (with a few exceptions). A recall is out of the question. Design changes must consider the existing equipment or replace it entirely. In short: you get one shot, make it count.
A lot of space infrastructure has done just that and is testament to those who designed it and put it in place, but without constant replacement and evolution everything starts to creak and move towards obsolescence. Though there was undoubtedly a plan of sustained maintenance at the outset, years down the line things always change as different pressures come to the fore. You look at the future of some satellite constellations and wonder how much more they’ve got to give.
So, what do DDK Positioning do to mitigate against impending obsolescence? Well firstly we deliver our GNSS augmentation over the Iridium NEXT constellation which began to phase out the previous Iridium SSC constellation in 2017 and was completed in 2019. The NEXT satellites have just begun their 15+ year mission so have plenty gas in the tanks. On top of that, Iridium is already planning the next generation and are committed to the evolution of their network.
Not only are the NEXT satellites, there’s also plenty of them in orbit. On top of the meshed network of 66 satellites which make up the primary constellation, there are an additional 9 in orbit spares with a further 6 ground spares available for launch. Though this is handy for both planned and unplanned maintenance in the near term, this will become invaluable in the future particularly as the satellites approach their design life. These spares will be used to ensure the constellation remains fully populated and therefore obsolescence is kept at bay.
The other key space-based ingredient to our positioning service is access to consistent, reliable GNSS signals. When it comes to GNSS satellites, the constellation that immediately springs to everyone’s mind through sheer constant exposure is GPS, however, consideration should also be given to GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. These constellations are not immune to obsolescence either and are constantly being refreshed, some more so than others. As these constellations are owned, not by private companies, but by , the influences of political change, economic change, world events or war are even more profound in the future of these systems.
At DDK Positioning our receivers can utilise all the available constellations and our Precise Point Positioning engine focuses on the use of three constellations. “Why not use them all?” you may ask. Well, it comes down to bang for your buck. Although we’ve trialled the use of four constellation in the solution, we found that three gives the optimum accuracy for the related data volumes and computational load. However, we know we can do this, it works and that we’ve got the option to swap out aging constellations for newer ones if required. As such we continue to monitor what’s going on up in space and are ready to react.
We’re all guilty of being so caught up in the here and now that we don’t always take time to consider the future, particularly when it comes to things we don’t see! Now might well be the perfect time to ask yourself:
- What satellite services am I currently using?
- What could happen to them in the future?
- And where does that leave me?
If the answers to the above concern you, or if you want to explore some options or solutions, please don’t hesitate to get in touch at info@ddkpositioning.com.
DDK Positioning have got you covered, and that’s why we confidently claim: Accuracy Everywhere!
by Cara Lewis | Dec 14, 2021 | Blog Post
Delivering GNSS Augmentation over a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellation provides both cost and efficiency benefits for vessels operating globally in the Offshore Energy sector. Using a LEO constellation reduces the risk of potential downtime due to its unique structure which provides a very robust, resilient and truly global communications service to deliver GNSS.
All existing GNSS Augmentation services currently use geo-stationary (GEO) satellites which are roughly 35,000km (22,000 miles) above the earth’s surface, whilst Iridium LEO satellites are approximately 780km (485 miles) above the Earth’s surface. One of the many key advantages of using a LEO satellite constellation over GEO is that LEO satellites offer stronger signals and faster connections through smaller antennas with lower power requirements.
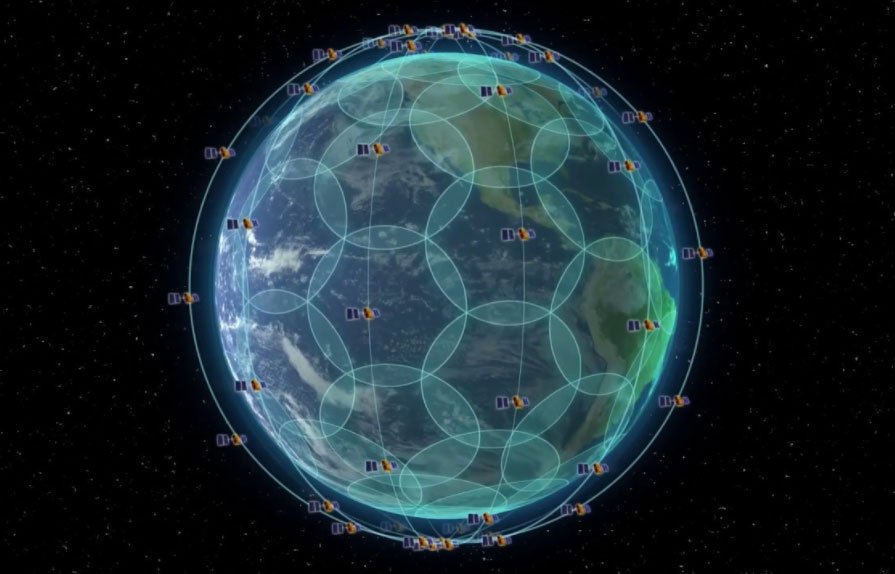
GEO satellites only provide coverage to around 65° N/S, with the GEO signal losing strength as the user tracks away from the equator. The LEO constellation provides truly global coverage and is a totally seamless service. The Iridium LEO service has 66 operational satellites plus 9 spares, it is a fully meshed service with built-in redundancy, with the user always seeing 2 to 4 LEO satellites at anytime, anywhere in world. There are 6 orbital planes spaced 30 degrees apart, 11 satellites per plane, 60 degrees coverage cone per satellite providing 100% coverage at the surface including coverage at the poles.
In addition, Iridium replaced all 66 operational and 9 spare satellites in 2019, without any disruption to the service and is one of the largest commercial satellite constellations.
The LEO network uses L-band frequencies to communicate with the users. These frequencies are more resilient to weather than the Ku / Ka band frequencies used by most GEO networks, providing reliable communications even in adverse conditions in the air, on the sea, or on the ground.
Together, the LEO satellites create a global mesh of coverage. In space, each satellite is cross-linked to four others, providing advantages in reliability and resiliency. These cross-links provide network optimisation and redundancy, ensuring that data can be rerouted and transmitted at the fastest possible speed no matter what happens on earth or in space. A vessel will always be connected to 2 – 4 satellites anywhere in the world thus reducing the risk of masking or blocking when operating near a large structure, such as a rig or platform.
GEO satellites are also subject to an increased risk of masking, as they remain in the same place above the earth’s surface, so if a user loses signal on the GEO satellite through masking the user will remain masked until they move. Whilst LEO satellites are in constant orbit resulting in less risk of masking.
LEO communications also provide the opportunity of a 2-way comms capability – a feature no existing providers currently have. This allows remote monitoring and provides direct [or automated] user quality control and diagnostic feedback, as well as advanced enable/disable for smart billing. Additional advantages include configuration and customisation of the receiver remotely and the ability to provide software upgrades, if needed, therefore reducing the need for an expensive engineer to attend the vessel offshore.
Current Precise Point Positioning (PPP) GNSS suppliers use GEO satellites to deliver augmentation to customers. GEO satellites are a single point of failure; having a new GNSS service delivered over LEO solves ‘redundancy’ problems. Until now, there has always been a risk of communication outages, which may result in costly downtime and with vessel rates costing thousands of USD per day, any amount of downtime can be very costly.
Iridium’s LEO satellite constellation is relied upon by the Federal and Civil Aviation Authorities for aircraft safety and is utilised to deliver the Global Maritime Distress Safety System for maritime safety. The same constellation is now being utilised to deliver PPP GNSS augmentation which provides a truly global, intelligent and independent service which can eliminate the single point of failure for the customer.
A LEO delivery mechanism provides a unique, global and resilient network minimising the customers exposure to risk, cost, and stress.
If you want to learn more about DDK Positioning’s unique global GNSS service, delivered via LEO, please contact us.




